《中国康复理论与实践》 ›› 2025, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 1342-1353.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2025.11.011
张梓寒1, 张家成1, 刘婧訸1, 陈宇航1, 吴丹1, 王荟荧1, 黄幸2, 常静玲1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-03
修回日期:2025-10-05
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-11-26
通讯作者:
常静玲
E-mail:ear6979@163.com
作者简介:张梓寒(1996-),女,汉族,重庆市人,博士研究生,主要研究方向:中医药防治脑病的临床与神经电生理研究。
基金资助:
ZHANG Zihan1, ZHANG Jiacheng1, LIU Jinghe1, CHEN Yuhang1, WU Dan1, WANG Huiying1, HUANG Xing2, CHANG Jingling1( )
)
Received:2025-06-03
Revised:2025-10-05
Published:2025-11-25
Online:2025-11-26
Contact:
CHANG Jingling
E-mail:ear6979@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 分析卒中后失语(PSA)患者在词图匹配任务下脑电脑功能网络特征。
方法 选取2018年1月至2021年12月东直门医院PSA患者18例(PSA组),并招募性别、年龄和受教育程度相匹配的健康受试者9例(对照组),采用汉语标准失语症检查法(CRRCAE)评估,采集基于汉语词图匹配的任务态脑电数据。对脑电信号进行溯源分析,构建功能连接矩阵,采用图论分析全局属性,并利用基于网络的统计分析(NBS)识别组间差异子网络,对全局属性与CRRCAE进行相关性分析。
结果 对照组不匹配条件下各频带全局属性显著高于PSA组和对照组(匹配条件)(P < 0.01)。PSA组在α频带存在额颞顶枕叶及边缘系统连接增强(23节点,31边,P < 0.05)和额颞边缘系统及基底节区连接降低(20节点,26边,P < 0.01)的子网络;β频带存在额颞叶、基底节及边缘系统连接增强的子网络(15节点,23边,P < 0.01);θ频带存在左侧额颞叶连接减弱(10节点,11边,P < 0.05)与右侧额颞叶连接增强(7节点,7边,P < 0.05)并存的子网络。匹配条件下,PSA组α频带和β频带全局属性均与阅读正相关(r = 0.511~0.650,均P < 0.05),θ频带局部效率和平均集群系数与复述呈负相关(r = -0.500~-0.505,均P < 0.05);不匹配条件下,PSA组α频带和β频带局部效率、平均集群系数均与阅读呈正相关(r = 0.522~0.642,均P < 0.05),α频带全局效率、局部效率与听理解呈正相关(r = 0.486~0.496,均P < 0.05)。任务态与静息态对比进一步揭示了PSA患者在α频带额叶及边缘系统(6节点,5边,P < 0.05)和β频带额颞顶枕叶及边缘系统(38节点,52边,P < 0.01)存在代偿性连接增强。
结论 PSA患者核心网络损伤特征为多频带全局属性异常降低和频带特异性网络异常重组,提示脑网络整体效能下降与局部代偿并存,为PSA的神经电生理评估及靶向干预提供了客观依据。
中图分类号:
张梓寒, 张家成, 刘婧訸, 陈宇航, 吴丹, 王荟荧, 黄幸, 常静玲. 基于功能连接探索卒中后失语患者的脑电脑功能网络特征[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(11): 1342-1353.
ZHANG Zihan, ZHANG Jiacheng, LIU Jinghe, CHEN Yuhang, WU Dan, WANG Huiying, HUANG Xing, CHANG Jingling. Characteristics of brain functional network based on electroencephalogram in post-stroke aphasia patients based on functional connectivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice, 2025, 31(11): 1342-1353.
表3
全局效率方差分析结果"
| 频带 | 对照组匹配 | 对照组不匹配 | PSA组匹配 | PSA组不匹配 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 0.15±0.01 | 0.16±0.04 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.15±0.01 | 335.057 | < 0.001 |
| β | 0.15±0.01 | 0.24±0.01 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.16±0.01 | 187.889 | < 0.001 |
| δ | 0.15±0.01 | 0.25±0.01 | 0.16±0.01 | 0.15±0.01 | 23.919 | < 0.001 |
| γ | 0.16±0.01 | 0.24±0.01 | 0.16±0.01 | 0.16±0.01 | 22.289 | < 0.001 |
| θ | 0.15±0.01 | 0.24±0.01 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.15±0.01 | 287.066 | < 0.001 |
表4
局部效率方差分析结果"
| 频带 | 对照组匹配 | 对照组不匹配 | PSA组匹配 | PSA组不匹配 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 0.23±0.01 | 0.35±0.01 | 0.23±0.01 | 0.23±0.02 | 22.226 | < 0.001 |
| β | 0.24±0.02 | 0.34±0.01 | 0.23±0.02 | 0.24±0.02 | 95.089 | < 0.001 |
| δ | 0.23±0.02 | 0.35±0.01 | 0.24±0.02 | 0.23±0.02 | 23.709 | < 0.001 |
| γ | 0.24±0.01 | 0.35±0.01 | 0.24±0.02 | 0.25±0.02 | 136.412 | < 0.001 |
| θ | 0.23±0.02 | 0.35±0.01 | 0.23±0.02 | 0.22±0.02 | 146.919 | < 0.001 |
表5
平均集群系数方差分析结果"
| 频带 | 对照组匹配 | 对照组不匹配 | PSA组匹配 | PSA组不匹配 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 0.19±0.02 | 0.28±0.01 | 0.19±0.02 | 0.18±0.01 | 117.944 | < 0.001 |
| β | 0.20±0.02 | 0.28±0.01 | 0.19±0.02 | 0.20±0.02 | 69.851 | < 0.001 |
| δ | 0.19±0.02 | 0.29±0.01 | 0.20±0.02 | 0.19±0.02 | 23.557 | < 0.001 |
| γ | 0.20±0.01 | 0.29±0.01 | 0.20±0.02 | 0.20±0.02 | 92.498 | < 0.001 |
| θ | 0.18±0.01 | 0.28±0.01 | 0.18±0.02 | 0.18±0.02 | 113.326 | < 0.001 |
表6
全局属性与CRRCAE各分项的相关性分析(r值)"
| 全局属性 | 条件 | 频带 | 听理解 | 复述 | 阅读 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全局效率 | 匹配 | α | 0.479a | -0.307 | 0.643b |
| β | 0.379 | -0.421 | 0.511a | ||
| δ | 0.340 | -0.073 | 0.525a | ||
| γ | 0.249 | -0.340 | 0.444 | ||
| θ | 0.232 | -0.330 | 0.369 | ||
| 不匹配 | α | 0.496a | -0.336 | 0.628b | |
| β | 0.385 | -0.425 | 0.448 | ||
| δ | 0.023 | -0.186 | 0.244 | ||
| γ | 0.311 | -0.362 | 0.219 | ||
| θ | 0.198 | -0.401 | 0.428 | ||
| 局部效率 | 匹配 | α | 0.431 | -0.382 | 0.650b |
| β | 0.382 | -0.381 | 0.580a | ||
| δ | 0.311 | -0.028 | 0.474a | ||
| γ | 0.261 | -0.382 | 0.486a | ||
| θ | 0.260 | -0.500a | 0.360 | ||
| 不匹配 | α | 0.486a | -0.327 | 0.642b | |
| β | 0.367 | -0.385 | 0.522a | ||
| δ | 0.124 | -0.202 | 0.320 | ||
| γ | 0.249 | -0.419 | 0.216 | ||
| θ | 0.334 | -0.381 | 0.455 | ||
| 平均集群系数 | 匹配 | α | 0.382 | -0.318 | 0.636a |
| β | 0.297 | -0.400 | 0.547a | ||
| δ | 0.220 | 0.046 | 0.373 | ||
| γ | 0.224 | -0.406 | 0.454 | ||
| θ | 0.229 | -0.505a | 0.359a | ||
| 不匹配 | α | 0.418 | -0.350 | 0.555a | |
| β | 0.367 | -0.441 | 0.534a | ||
| δ | 0.035 | -0.166 | 0.256 | ||
| γ | 0.025 | -0.326 | 0.108 | ||
| θ | 0.319 | -0.418 | 0.413 |
图2
两组α频带差异脑网络 注: A.连接减弱的脑网络;B.连接增强的脑网络。圆球代表网络节点,不同颜色代表不同脑区,红色为前额叶、橙色为额叶、绿色为皮质下、浅蓝色为顶叶、深蓝色为颞叶、紫色为枕叶。灰色的连线代表连接下降的边,黄色连线代表连接增强的边。 连接减弱:PreCG.L,中央前回(左);PoCG.L,中央后回(左);SFGdor.L,额上回背侧(左);SFGmed.L,额上回内侧(左);SFGmed.R,额上回内侧(右);MFG.L,额中回(左);IFGoperc.L,额下回盖部(左);IFGtriang.L,额下回三角部(左);ORBinf.L,眶部下侧(左);ORBmid.L,眶部中部(左);ROL.L,中央旁回(左);ACG.L,前扣带回(左);ACG.R,前扣带回(右);DCG.R,后扣带回(右);CAU.R,尾状核(右);PAL.R,苍白球(右);HES.L,颞横回(赫氏回,左);STG.L,颞上回(左);TPOsup.L,颞顶枕联合区上侧(左);TPOmid.L,颞顶枕联合区中部(左)。 连接增强:ORBsupmed.L,眶部上内侧(左);ACG.L,前扣带回(左);REC.L,直回(左);REC.R ,直回(右);ROL.L,中央旁回(左);PCG.L,中央后回(左);ANG.L,角回(左);PCUN.L,楔前叶(左);PCUN.R,楔前叶(右);SPG.R,顶上小叶(右);PCL.R,小脑蚓部(右);CAL.L,距状裂周围皮质(左);CUN.L,楔叶(左);CUN.R,楔叶(右);LING.L,舌回(左);MOG.L,枕中回(左);MOG.R,枕中回(右);SOG.R,枕上回(右);HES.L,颞横回(赫氏回,左);HES.R,颞横回(赫氏回,右);STG.R,颞上回(右);MTG.L,颞中回(左);THA.L,丘脑(左)。"
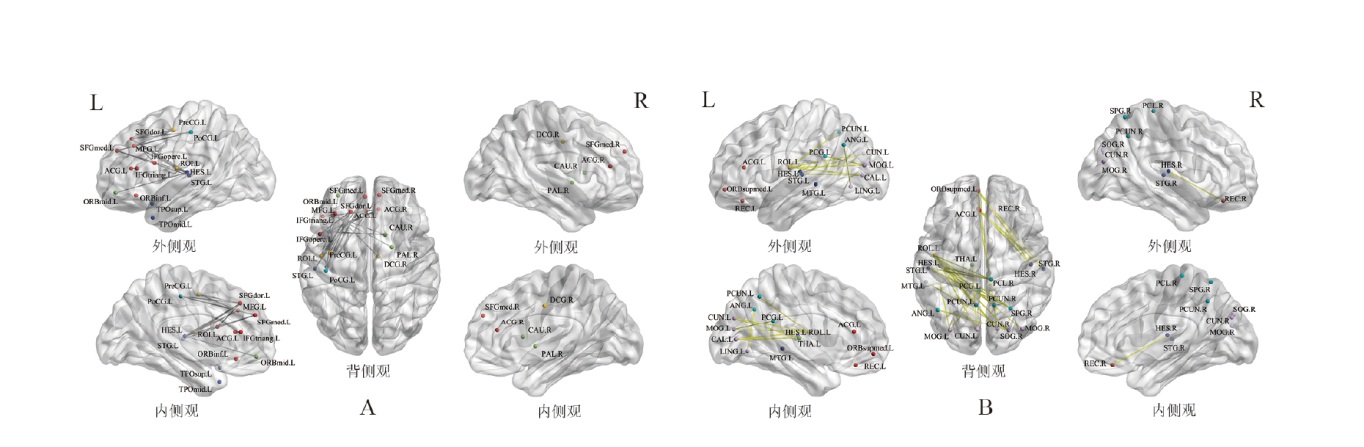
图3
两组β频带功能连接差异 注: 圆球代表网络节点,不同颜色代表不同脑区,红色为前额叶、橙色为额叶、绿色为皮质下、浅蓝色为顶叶、深蓝色为颞叶、紫色为枕叶。黄色连线代表连接增强的边。SFGdor.L,额上回背侧(左);MFG.L,额中回(左);SFGmed.L,额上回内侧(左);SFGmed.R,额上回内侧(右);ORBsup.R,眶部上侧(右);ORBmid.R,眶部中部(右);ORBinf.R,眶部下侧(右);ORBsupmed.R,眶部上内侧(右);OLF.R,嗅皮质(右);REC.R,直回(右);ACG.L,前扣带回(左);ACG.R,前扣带回(右);CAU.L,尾状核(左);CAU.R,尾状核(右);PUT.R,壳核(右)。"
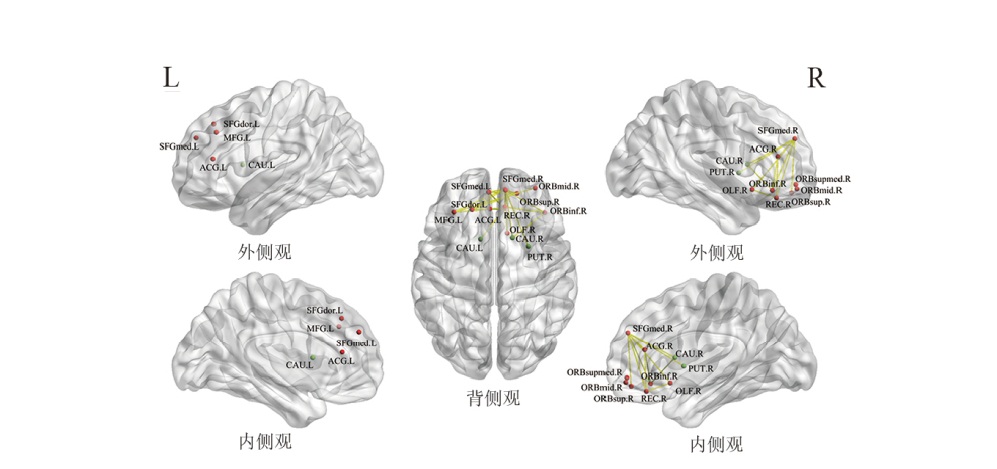
图4
两组θ频带功能连接差异 注: A.连接减弱的脑网络;B.连接增强的脑网络。圆球代表网络节点,不同颜色代表不同脑区,红色为前额叶、橙色为额叶、绿色为皮质下、浅蓝色为顶叶、深蓝色为颞叶、紫色为枕叶。灰色的连线代表连接下降的边,黄色连线代表连接增强的边。 连接减弱:MFG.L,额中回(左);IFGoperc.L,额下回盖部(左);IFGtriang.L,额下回三角部(左);ROL.L,中央旁回(左);SFGmed.L,额上回内侧(左);SFGmed.R,额上回内侧(右);ORBsupmed.L,眶部上内侧(左);ACG.R,前扣带回(右);HES.L,颞横回(左);STG.L,颞上回。 连接增强:ROL.R,中央旁回(右);ORBsupmed.L,眶部上内侧(左);ORBsupmed.R,眶部上内侧(右);ACG.L,前扣带回(左);ACG.R,前扣带回(右);STG.R,颞上回(右);HES.R,颞横回(赫氏回,右)。"
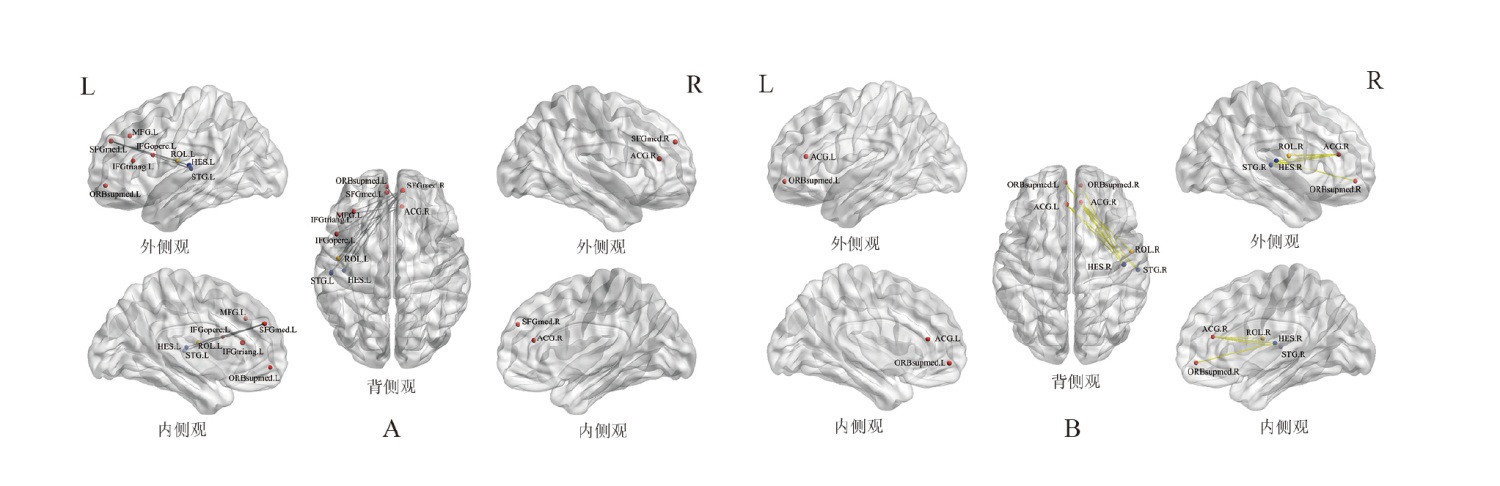
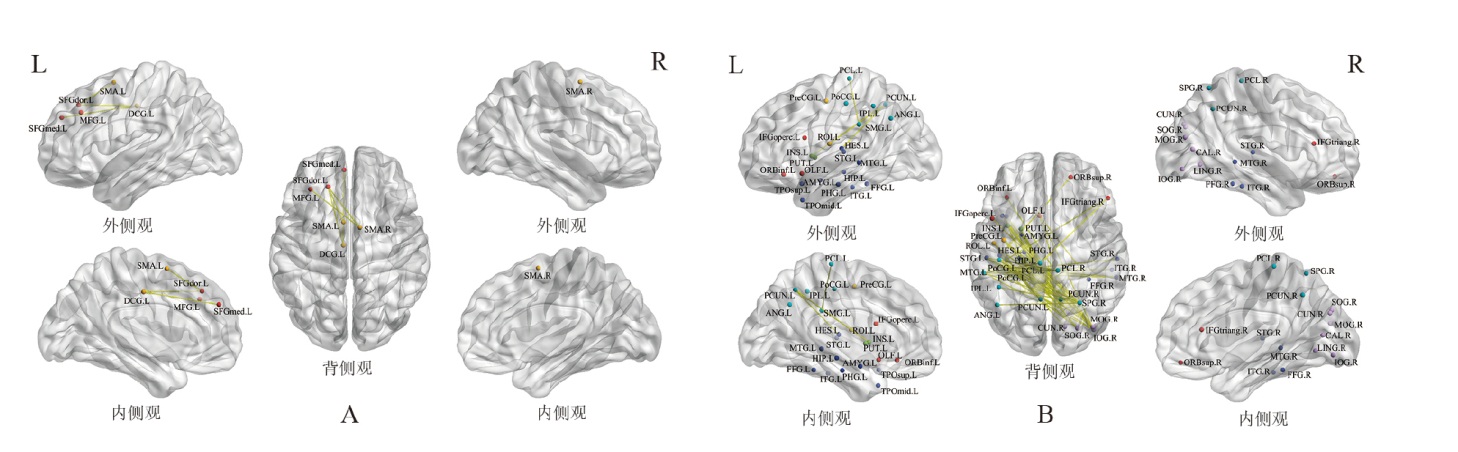
图5
PSA组任务态与静息态脑电功能连接差异 注: A.α频带连接增强的脑网络;B.β频带连接增强的脑网络。圆球代表网络节点,不同颜色代表不同脑区,红色为前额叶、橙色为额叶、绿色为皮质下、浅蓝色为顶叶、深蓝色为颞叶、紫色为枕叶。黄色连线代表连接增强的边。 α频带:SFGmed.L,额上回内侧(左);SFGdor.L,额上回背侧(左);MFG.L,左侧额中回(左);SMA.L,辅助运动区(左);SMA.R,辅助运动区(右);DCG.L,后扣带回(左)。 β频带:ORBinf.L,眶部下侧(左);ORBsup.R,右侧眶部上侧(右);IFGoperc.L,左侧额下回盖部(左);IFGtriang.R,额下回三角部(右);OLF.L,嗅皮质(左);PreCG.L,中央前回(左);ROL.L,中央旁回(左);HIP.L,海马(左);PHG.L,海马旁回(左);AMYG.L,杏仁核(左);FFG.L,梭状回(左);FFG.R,梭状回(右);ITG.L,颞下回(左);ITG.R,颞下回(右);HES.L,颞横回(赫氏回,左);STG.L,颞上回(左);STG.R,颞上回(右);MTG.L,颞中回(左);MTG.R,颞中回(右);TPOsup.L,颞顶枕联合区上侧(左);TPOmid.L,颞顶枕联合区中部(左);CAL.R,距状裂周围皮质(右);CUN.R,楔叶(右);LING.R,舌回(右);SOG.R,枕上回(右);MOG.R,枕中回(右);IOG.R,枕下回(右);PoCG.L,中央后回(左);PCUN.L,楔前叶(左);PCUN.R,楔前叶(右);PCL.L ,小脑蚓部(左);PCL.R,小脑蚓部(右);ANG.L,角回(左);IPL.L,顶下小叶(左);SPG.R,顶上小叶(右);SMG.L,缘上回(左);PUT.L,壳核(左);INS.L,岛叶(左)。"
| [1] |
GINEX V, GILARDONE G, VIGANÒ M, et al. Interaction between recovery of motor and language abilities after stroke[J]. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2020, 101(8): 1367-1376.
doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2020.04.010 |
| [2] |
FILIPSKA-BLEJDER K, ZIELIŃSKA J, ZIELIŃSKI M, et al. How does aphasia affect quality of life? Preliminary reports[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(24): 7687.
doi: 10.3390/jcm12247687 |
| [3] |
KAO S K, CHAN C T. Increased risk of depression and associated symptoms in poststroke aphasia[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 21352.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72742-z |
| [4] |
JIANG Z, KUHNKE P, STOCKERT A, et al. Dynamic reorganization of task-related network interactions in post-stroke aphasia recovery[J]. Brain, 2025, 148(10): 3563-3575.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf036 |
| [5] | 罗淇, 王霞, 姜孟. 脑功能网络分析在失语症诊疗中的应用:病理机制分析、临床诊断与疗效评价[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2025, 63(8): 111-126. |
| LUO Q, WANG X, JIANG M. Application of functional brain network analysis in aphasia:insights into neuropathological mechanisms,clinical diagnosis,and assessment of therapeutic outcome[J]. J Shandong Univ (Health Sciences), 2025, 63(8): 111-126. | |
| [6] |
BABAEEGHAZVINI P, RUEDA-DELGADO L M, GOOIJERS J, et al. Brain structural and functional connectivity: a review of combined works of diffusion magnetic resonance imaging and electro-encephalography[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2021, 15: 721206.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.721206 |
| [7] |
SARMUKADAM K, BEHROOZMAND R. Aberrant beta-band brain connectivity predicts speech motor planning deficits in post-stroke aphasia[J]. Cortex, 2022, 155: 75-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2022.07.001 pmid: 35973239 |
| [8] | 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组, 中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52(9): 710-715. |
| Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Stroke Society. Diagnostic criteria of cerebrovascular diseases in China (version 2019)[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2019, 52(9): 710-715. | |
| [9] |
常静玲, 张斌龙, 谭中建, 等. 基于汉语高频名词下词图匹配语义判断任务的设计与运用范式[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2018, 24(8): 917-923.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.08.010 |
| CHANG J L, ZHANG B L, TAN Z J, et al. Design and pilot study of word-picture matching semantic judgment task based on Chinese High frequency nouns[J]. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract, 2018, 24(8): 917-923. | |
| [10] |
DELORME A, MAKEIG S. EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2004, 134(1): 9-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009 |
| [11] | OOSTENVELD R, FRIES P, MARIS E, et al. FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data[J]. Comput Intell Neurosci, 2011, 2011: 156869. |
| [12] |
WANG J, WANG X, XIA M, et al. GRETNA: a graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2015, 9: 386.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00386 pmid: 26175682 |
| [13] |
XIA M, WANG J, HE Y. BrainNet Viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e68910.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068910 |
| [14] | 李胜利, 肖兰, 田鸿, 等. 汉语标准失语症检查法的编制与常模[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2000, 6(4): 18-20, 49. |
| LI S L, XIAO L, TIAN H, et al. Introduction to Chinese Standard Aphasia Examination[J]. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract, 2000, 6(4): 18-20, 49. | |
| [15] |
KOUTI M, ANSARI-ASL K, NAMJOO E. EEG dynamic source imaging using a regularized optimization with spatio-temporal constraints[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2024, 62(10): 3073-3088.
doi: 10.1007/s11517-024-03125-9 |
| [16] |
PIAI V, OOSTENVELD R, SCHOFFELEN J M, et al. The impact of CSF-filled cavities on scalp EEG and its implications[J]. Psychophysiology, 2024, 61(10): e14624.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.v61.10 |
| [17] |
ZHENG K, JIANG C, XU Q, et al. A concentric ring microneedle electrode with low contact impedance for close sources laplacian EEG recording[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2025, 72(5): 1532-1541.
doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3511596 |
| [18] |
VATINNO A A, SIMPSON A, RAMAKRISHNAN V, et al. The prognostic utility of electroencephalography in stroke recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neurorehabil Neural Repair, 2022, 36(4-5): 255-268.
doi: 10.1177/15459683221078294 |
| [19] |
KHAMECHIAN M B, DALIRI M R. Frequency modulation of cortical rhythmicity governs behavioral variability, excitability and synchrony of neurons in the visual cortex[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 20914.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25264-5 pmid: 36463385 |
| [20] |
MENESSE G, TORRES J J. Information dynamics of in silico EEG brain waves: Insights into oscillations and functions[J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2024, 20(9): e1012369.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012369 |
| [21] |
DIRANI J, PYLKKÄNEN L. The time course of cross-modal representations of conceptual categories[J]. Neuroimage, 2023, 277: 120254.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120254 |
| [22] |
ARRIGONI E, RAPPO E, PAPAGNO C, et al. Neural correlates of semantic interference and phonological facilitation in picture naming: a systematic review and coordinate-based meta-analysis[J]. Neuropsychol Rev, 2025, 35(1): 35-53.
doi: 10.1007/s11065-024-09631-9 |
| [23] |
秦天鹏, 生慧, 岳路, 等. 脑电信号情绪识别研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(15): 38-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2209-0429 |
|
QIN T P, SHENG H, YUE L, et al. Review of research on emotion recognition based on EEG signals[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2023, 59(15): 38-54.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2209-0429 |
|
| [24] |
JUNKER F B, SCHMIDT-WILCKE T, SCHNITZLER A, et al. Temporal dynamics of oscillatory activity during nonlexical language decoding: evidence from Morse code and magnetoencephalography[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2023, 44(17): 6185-6197.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.26505 pmid: 37792277 |
| [25] |
NESS T, LANGLOIS V J, NOVICK J M, et al. Theta-band neural oscillations reflect cognitive control during language processing[J]. J Exp Psychol Gen, 2024, 153(9): 2279-2298.
doi: 10.1037/xge0001621 pmid: 39235889 |
| [26] |
DALTON S G H, CAVANAGH J F, RICHARDSON J D. Spectral resting-state EEG (rsEEG) in chronic aphasia is reliable, sensitive, and correlates with functional behavior[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2021, 15: 624660.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.624660 |
| [27] |
SNYDER D B, SCHMIT B D, HYNGSTROM A S, et al. Electroencephalography resting-state networks in people with stroke[J]. Brain Behav, 2021, 11(5): e02097.
doi: 10.1002/brb3.v11.5 |
| [28] |
SHAH-BASAK P, SIVARATNAM G, TETI S, et al. Electrophysiological connectivity markers of preserved language functions in post-stroke aphasia[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2022, 34: 103036.
doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103036 |
| [29] |
ZALESKY A, FORNITO A, BULLMORE E T. Network-based statistic: identifying differences in brain networks[J]. Neuroimage, 2010, 53(4): 1197-1207.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.041 pmid: 20600983 |
| [30] |
KOCSIS Z, JENISON R L, TAYLOR P N, et al. Immediate neural impact and incomplete compensation after semantic hub disconnection[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 6264.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42088-7 pmid: 37805497 |
| [31] |
ZHU W, DENG S, JIANG H, et al. Application of diffusion tensor imaging in the diagnosis of post-stroke aphasia: a meta-analysis and systematic review[J]. Front Psychol, 2023, 14: 1140588.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1140588 |
| [32] |
RABINI G, UBALDI S, FAIRHALL S L. Task-based activation and resting-state connectivity predict individual differences in semantic capacity for complex semantic knowledge[J]. Commun Biol, 2023, 6(1): 1020.
doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05400-1 pmid: 37813935 |
| [33] |
ROLLS E T, DECO G, HUANG C C, et al. Human amygdala compared to orbitofrontal cortex connectivity, and emotion[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2023, 220: 102385.
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102385 |
| [34] | LANCIEGO J L, OBESO J A. Functional neuroanatomy of the normal and pathological basal ganglia[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2024: a041617. |
| [35] |
LEONARDS C A, HARRISON B J, JAMIESON A J, et al. A distinct intra-individual suppression subnetwork in the brain's default mode network across cognitive tasks[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2023, 33(8): 4553-4561.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac361 |
| [36] |
GENG H, XU P, ALEMAN A, et al. Dynamic organization of large-scale functional brain networks supports interactions between emotion and executive control[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2024, 40(7): 981-991.
doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01168-w pmid: 38261252 |
| [37] |
MEULENBERG C J W, REHFELD K, JOVANOVIĆ S, et al. Unleashing the potential of dance: a neuroplasticity-based approach bridging from older adults to Parkinson's disease patients[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2023, 15: 1188855.
doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1188855 |
| [38] | ORPELLA J, FLICK G, ASSANEO M F, et al. Reactive inhibitory control precedes overt stuttering events[J]. Neurobiol Lang (Camb), 2024, 5(2): 432-453. |
| [39] |
HELL F, EIßNER A, MEHRKENS J H, et al. Subthalamic oscillatory activity during normal and impaired speech[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2023, 149: 42-50.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2023.02.166 pmid: 36893498 |
| [40] |
ZHANG J, LI H, QU J, et al. Language proficiency is associated with neural representational dimensionality of semantic concepts[J]. Brain Lang, 2024, 258: 105485.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2024.105485 |
| [41] |
GAO C, WU J, CHENG Y, et al. Continuous theta-burst stimulation demonstrates language-network-specific causal effects on syntactic processing[J]. Neuroimage, 2025, 306(2025): 121014.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2025.121014 |
| [42] |
LI Z, ZHOU Z, WANG X, et al. Neural correlates of analogical reasoning on syntactic patterns[J]. J Cogn Neurosci, 2024, 36(5): 854-871.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_02115 |
| [43] |
樊瑞文, 李晓琳, 黄幸, 等. 基于语言双流模型的卒中后失语右脑功能网络研究[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2020, 26(5): 572-578.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2020.05.016 |
| FAN R W, LI X L, HUANG X, et al. Functional connectivities in right hemisphere for post-stroke aphasia: based on dual stream model[J]. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract, 2020, 26(5): 572-578. | |
| [44] |
KUHNKE P, BEAUPAIN M C, AROLA J, et al. Meta-analytic evidence for a novel hierarchical model of conceptual processing[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2023, 144: 104994.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104994 |
| [1] | 骆丹丹, 沈敏, 王素娟, 邱翁歆, 张宇轩, 吴蕴, 王圣虓. 汉语发展性阅读障碍儿童全脑静息态功能连接的特征分析[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(9): 1023-1031. |
| [2] | 李红卫, 黄彬彬, 朱传花, 李伟. 经颅直流电刺激对意识障碍患者脑功能网络方向性连接的影响[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(9): 1050-1056. |
| [3] | 张梓寒, 管津智, 黄幸, 周莉, 张雅宣, 张蒙园, 常静玲. 卒中后失语患者汉语词图匹配任务态脑电的时域及时频特征[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(8): 947-957. |
| [4] | 李峤桢, 冯枫, 杜霞, 邵雯, 高咪, 惠琳娜, 袁华, 孙晓龙. 脊髓损伤神经病理性疼痛的脑电信号特征[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(7): 830-837. |
| [5] | 李鑫磊, 魏伟, 宋健, 赵雨晴, 孔维橙, 蔡嘉玉, 施浩然, 薛偕华. 静息态脑电图在脑卒中患者上肢运动功能评估中的应用[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(4): 448-457. |
| [6] | 顾剑鹏, 宋玉磊, 殷海燕, 尹婷婷, 孙凤仪, 杨冰清, 赵鸣晖, 徐桂华, 柏亚妹. 定量脑电图在轻度认知障碍数字化筛查中的应用[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(11): 1314-1321. |
| [7] | 陈宇航, 杨瑜爱, 卢轩禹, 王昱航, 张蒙园, 张梓寒, 王荟荧, 常静玲. 卒中后失语和卒中后抑郁自发脑活动改变的静息态功能磁共振成像Meta分析[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(10): 1143-1155. |
| [8] | 徐胜, 张敏, 杨青青, 王庆雷, 耿阿燕, 王彤, 郭川. 功能性电刺激手摇车对脑卒中患者脑网络功能连接的功能性近红外光谱研究[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(10): 1181-1187. |
| [9] | 赵新颖, 于福达, 王慧, 李晓峰, 张笑娣, 白冬儿, 李嘉民. 不同脑梗死部位及神经功能缺损程度的脑电图功率谱特征[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2025, 31(10): 1188-1193. |
| [10] | 张哲, 董献文, 徐成铭, 胡文静, 贺婷丽, 崔鑫鑫, 徐红艳, 周章盈, 韩雅男. 近10年脑电图应用于孤独症谱系障碍领域研究的文献计量分析[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(6): 693-700. |
| [11] | 陈园月, 李加斌, 蒯凤, 彭丽丽, 项洁. 多通道功能性电刺激结合任务导向训练对脑卒中上肢偏瘫患者脑功能网络的即刻影响[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(4): 462-467. |
| [12] | 黄幸, 常静玲, 张梓寒, 李颖. 卒中后失语工作记忆的事件相关电位及时频特征[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(3): 316-325. |
| [13] | 马晓晨, 李淑璠, 贾舒祺, 刘聪, 张振宇, 韩东洋. 认知障碍老年人身体活动、认知功能与睡眠质量的关系:基于静息脑电的中介效应分析[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(12): 1442-1451. |
| [14] | 蔡丝妍, 范颖洁, 田慧芳, 夏春亚, 张娟, 苏敏. 音乐治疗基础上联合经颅直流电刺激对失眠效果的随机对照试验[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(10): 1193-1202. |
| [15] | 刘冬, 徐子涵, 李江, 鞠萍. M1区联合背外侧前额叶高频重复经颅磁刺激对脊髓损伤后神经病理性疼痛患者脑电图θ振幅的效果[J]. 《中国康复理论与实践》, 2024, 30(1): 87-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|
||
